- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
20/10/2024 at 15:19 #3365
1. Introduction
Ceramides are naturally occurring lipids present in the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin. These essential molecules are crucial for maintaining the skin's barrier function by locking in moisture and protecting against environmental aggressors. However, as we age or due to external factors like harsh weather or pollution, ceramide levels can decline, leading to dry and compromised skin. Incorporating ceramides into skincare and haircare formulations can help counteract these effects, offering long-term benefits for skin and hair health.
2. Benefits at a Glance
Reinforces the natural lipid barrier in dry and aging skin.
Enhances long-term moisturization and protects against environmental factors.
Repairs and protects damaged hair, improving mechanical properties, vitality, combability, and shine.
Contains human skin-identical molecules for optimal compatibility and efficacy.
3. Properties of Ceramides
Ceramide III and Ceramide IIIB are instrumental in renewing the skin's protective layer and forming a robust barrier against moisture loss. These human skin-identical molecules are particularly effective in providing long-term protection and repair for sensitive and dry skin, making them ideal for skincare formulations aimed at enhancing barrier function and hydration.
4. Differences Between Ceramide III and Ceramide IIIB
Ceramide III: This molecule consists of a phytosphingosine backbone acylated with a saturated fatty acid (stearic acid). Among the eight possible stereoisomers, only the 2S,3S,4R configuration is naturally found in human skin.
Ceramide IIIB: While also featuring a phytosphingosine backbone, Ceramide IIIB is acylated with oleic acid, introducing an unsaturated bond in its fatty acid chain, distinguishing it from Ceramide III.
Efficacy studies have shown that Ceramide III is effective at concentrations as low as 0.05%. Depending on the skin type and desired outcome, the recommended concentration ranges from 0.05% to 0.5%, with some formulations requiring up to 1%.
5. 3D Skin Test
The efficacy of Ceramide III and IIIB can be further validated through advanced 3D skin testing, which mimics the complex structure of human skin. These tests provide insights into the long-term benefits and performance of ceramides in skincare applications, confirming their role in enhancing skin barrier function and hydration.
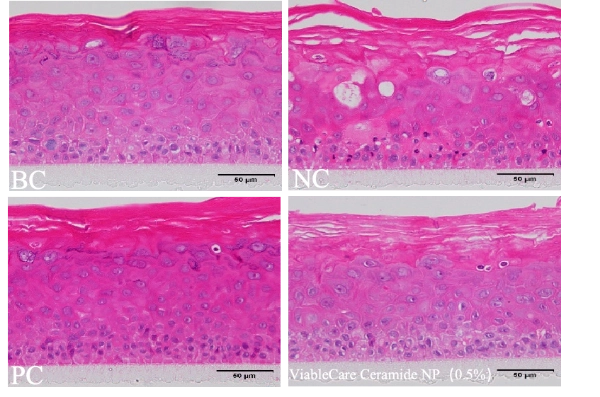
ViableCare Ceramide NP promotes the repair of damaged epidermal 3D skin models.
Repair improveneme reaches to 4.9%.
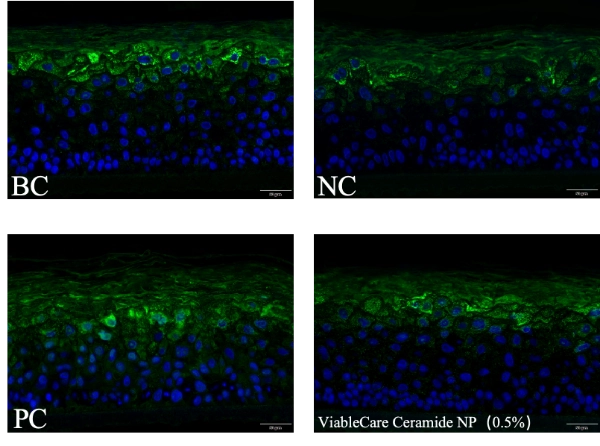
The intensity of fluorescence signal was enhanced after ViableCare Ceramide NP repair, skin barrier repair rate reached 50%.
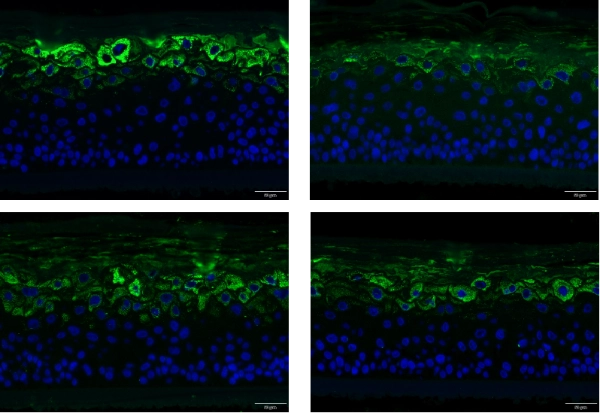
ViableCare Ceramide NP can effectively promote the expression of FLG, and the repair improvement rate is 80%.
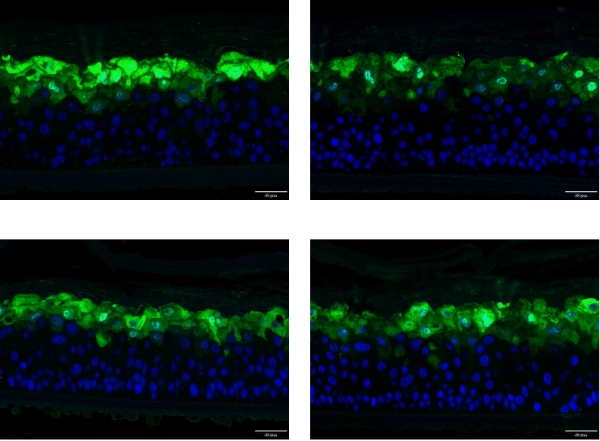
ViableCare Ceramide NP in promoting LOR protein expression was similar to that of PC
6. Preparation Methods
Emulsions
Ceramides are amphiphilic molecules and can be incorporated into the lamellar liquid crystalline structures built up by emulsifier and consistency agents in the external water phase of cosmetic O/W emulsions. In general, ceramides are nearly insoluble in common cosmetic oils at room temperature. They can be clearly solved in most cosmetic oils by heating up to 90°C. The oils differ in the temperature at which the mixture becomes turbid again while cooling. The solubility in the oil phase seems not to be crucial for the stability of the formulation with respect to recrystallisation of ceramide. It is very important, however, that the ceramide is clearly and completely solved in the oil phase at the beginning of and during the homogenization step. Towards this end both the water phase and the oil phase should have a temperature of at least 90°C. Oils with a good solvency for ceramides should be chosen, e. g. PPG-3 Myristyl Ether, C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate and Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride. To obtain a pleasant skin feel it is suggested to combine those oils with low viscosity oils such as Ethylhexyl Palmitate, Decyl Cocoate and Isopropyl Palmitate.
Ceramide III, especially at higher concentrations (0.5% and higher), has a strong negative influence on the freeze stability of an O/W emulsion. By choosing polar oils, adding Carbomer and/or increasing the oil phase up to 25% the freeze stability can be optimized. Ceramide IIIB has a significantly better solubility in cosmetic oils and a much lower tendency to recrystallise. By following the above mentioned guidelines formulations will have a long-term stability against recrystallisation of ceramide.
Clear aqueous formulations
Ceramide III and Ceramide IIIB show a very low solubility in water and besides Ceramide III has a very high melting point. Nevertheless it is possible to develop clear aqueous formulations with Ceramide III and Ceramide IIIB (for example shampoos, clear Leave in Conditioners). For the solubilization of the ceramides it is necessary to find a suitable solubilizer which can be heated up to a temperature of about 90°C or even higher to ensure that the ceramides are melted completly. During the addition of the other ingredients of the formulation (surfactants, water, conditioners, thickeners and so on) the temperature must be kept at 80 – 85°C.
Suitable solubilizers for the ceramides are PEG-40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil, Polyglyceryl-3 Caprate, Polyglyceryl-4 Caprate or Sodium Lauroyl Lactylate. For a clear Leave in Conditioner PEG-40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil is especially suitable, for a shampoo formulation Poly- glyceryl-3 Caprate or Polyglyceryl-4 Caprate also can be used. Another problem of shampoo formulations is the tendency of Ceramide III to crystallise after 1 – 3 months. This crystallisation can be avoided if a combination of two or more different ceramides (Ceramide III, IIIB, VI) are used.
Emulsion based Hair care formulation
The production of an emulsion based hair care formulation (for example hair rinses or cream conditioners) is comparable to that described before for an O/W-Emulsion. The water phase and the oil phase (emulsifier, consistency enhancer, ceramides and possible small amouts of emollients) must be heated up to 90°C to ensure that the ceramides are clearly solubilized. Monomeric Quats or Sodium Lauroyl Lactylate are especially suitable to improve the stability of hair rinses with ceramides.
7. Recommended Usage Concentration
The recommended concentration for Ceramide III or Ceramide IIIB ranges from 0.05% to 1.0%, depending on the product and desired effects.
8. Applications
Ceramide III and Ceramide IIIB are versatile ingredients suitable for a wide range of applications:
O/W Creams and Lotions:
Moisturizing formulations
Skin repair products
Baby care
Facial care
Sun care
Hair Care Products:
Hair rinses
Leave-in conditioners
Conditioning shampoos
9. Packaging
Ceramide III: 0.50 kg/bottle
Ceramide IIIB: 0.50 kg/bottle
Related Products:
1. L-Tyrosine
2. Nicotinamide
http://www.viablife.ne
Viablife -
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.


